The backbone of the Internet: Common Internet Infrastructure
The Internet is essential to modern life, connecting billions of people and devices worldwide. But have you ever wondered what makes it work? The Internet relies on a complex infrastructure of physical and digital components that work together seamlessly. Let’s dive into the key elements that power the global web.
Table of Contents
TogglePhysical Internet Infrastructure: The Internet’s Highway
The Internet relies on physical hardware to transmit data across the globe. These include:
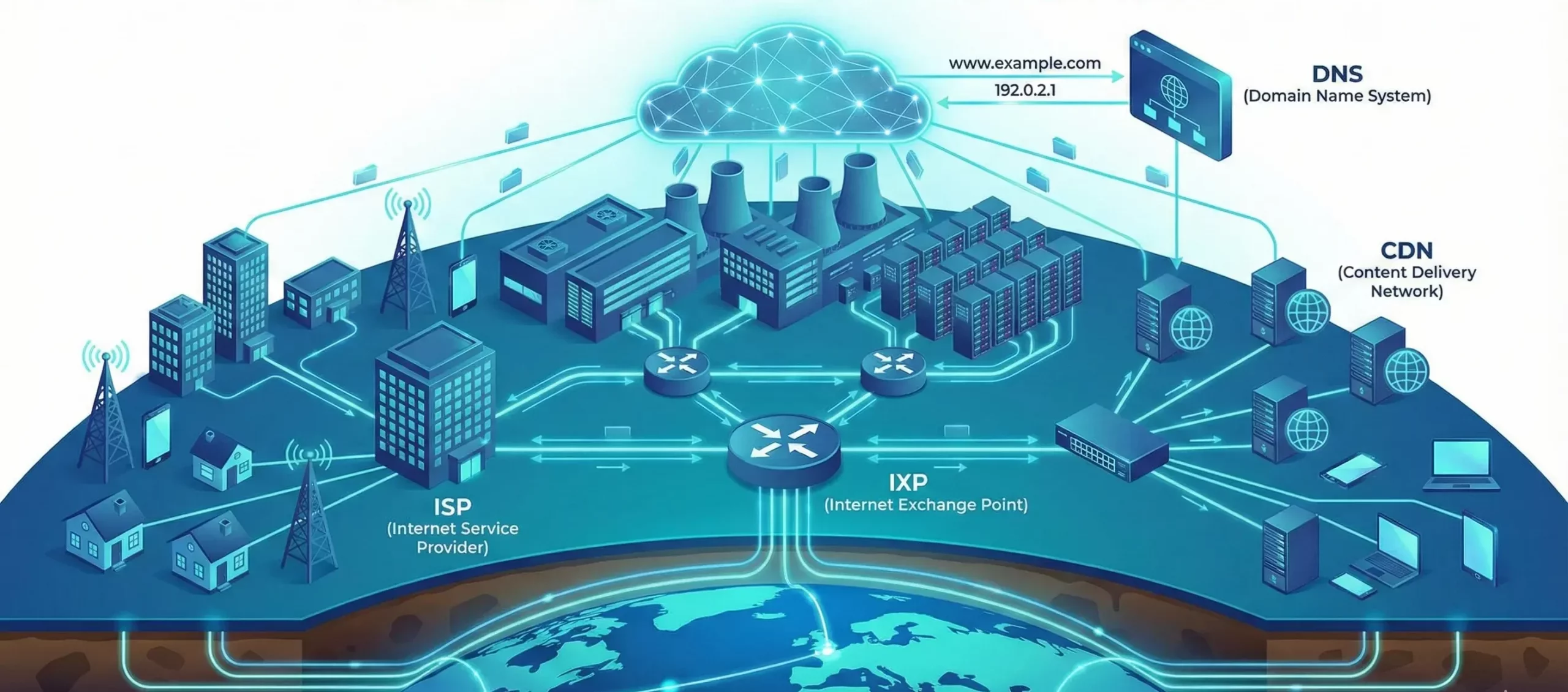
- Fiber-Optic Cables – The backbone of Internet connectivity, carrying data at high speeds across cities, countries, and even oceans.
- Submarine Cables – Underwater fiber-optic cables that connect continents, ensuring global data exchange.
- Data Centers – Large facilities housing servers that store, process, and distribute data for websites, apps, and cloud services.
- Internet Exchange Points (IXPs) – Critical hubs where different networks interconnect, improving efficiency and reducing data transmission delays.
- Satellite Networks – Used to provide Internet access in remote areas where fiber or traditional cables are not feasible.
Networking Components: Brains Behind Connectivity
Beyond the physical hardware, various networking devices help route and manage Internet traffic:
- Routers – Direct data packets between different networks, determining the best path for transmission.
- Switches – Connect devices within a local network, facilitating internal communication.
- Modems – Convert digital signals for transmission over telephone or fiber-optic lines.
- Load Balancers – Distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers to prevent overload and enhance performance.
Internet Service Providers (ISPs): The Gateway to the Web
ISPs are companies that provide Internet access to users. They operate on different levels:
- Tier 1 ISPs – Large global providers that form the core Internet backbone.
- Tier 2 ISPs – Regional providers that connect to Tier 1 networks.
- Tier 3 ISPs – Local ISPs that deliver Internet services directly to homes and businesses.
Protocols and Standards: The Language of the Internet
To ensure smooth communication, the Internet operates on standardized protocols:
- Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) – The foundation of data exchange, ensuring information is sent and received accurately.
- Domain Name System (DNS) – Translates human-readable web addresses (e.g., google.com) into machine-readable IP addresses.
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/HTTPS) – Governs web browsing and data exchange over the web.
- Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) – Helps ISPs determine the best path for routing Internet traffic.
- Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) – Enables email communication between servers.
Cloud Computing & Content Delivery: Speeding Up the Web
With increasing demand for speed and efficiency, cloud services and content delivery networks (CDNs) play a major role:
- Cloud Services (AWS, Google Cloud, Azure) – Offer storage, computing power, and infrastructure over the Internet.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) – Store cached content across global servers to reduce load times and improve website performance.
Cybersecurity & Governance: Keeping the Internet Safe
To maintain security and stability, various systems and organizations manage Internet governance:
- Firewalls – Protect networks by filtering unauthorized traffic.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) – Encrypt Internet connections to enhance privacy and security.
- Regulatory Bodies (ICANN, IETF, ITU) – Oversee domain name registration, protocol development, and global Internet policies.
Final Thoughts: Internet Infrastructure
The Internet is more than just websites and social media; it’s a vast and intricate system powered by physical and digital infrastructure. From fiber-optic cables to cloud computing, every component plays a crucial role in keeping the world connected. As technology evolves, so will the Internet’s backbone, paving the way for faster and more efficient global communication.
Trusted IPv4 Leasing for Business Growth
Get enterprise-grade IPv4 space quickly, with seamless deployment and end-to-end management.
A clear comprehension of the discrepancies between IP reputation and IP risk score constitutes a critical prerequisite for effective cybersecurity Read more
Organisations increasingly rely on IP risk scores. They use them to assess threat levels. They reduce fraud losses. They strengthen Read more
The current era faces IPv4 address scarcity. Organizations must verify IP block risk scores. Tools like i.lease help complete this Read more



