What Is a Regional Internet Registry (RIR)?
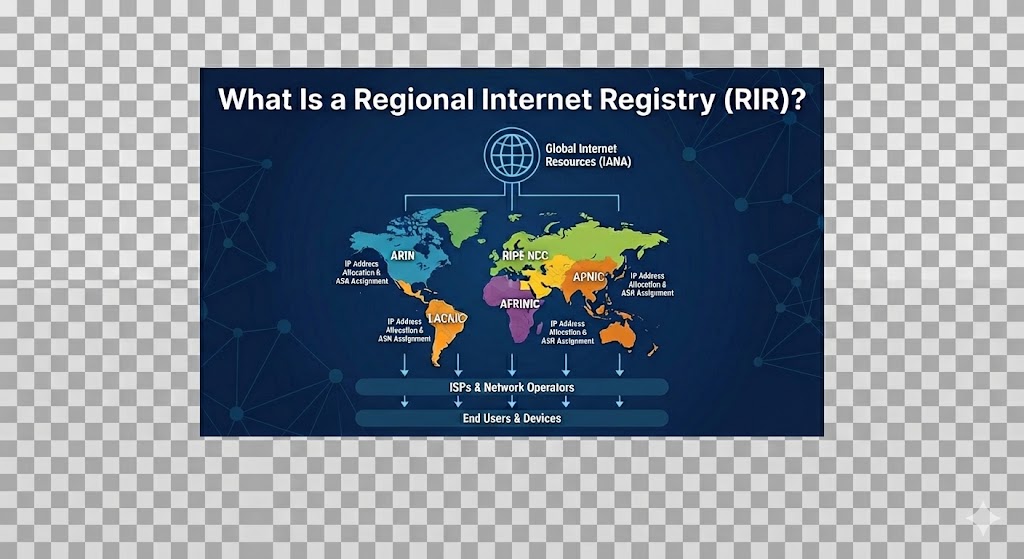
Table of Contents
A Regional Internet Registry (RIR) is an organization responsible for the allocation and management of Internet number resources within a specific geographic region. These resources primarily include IP addresses (both IPv4 and IPv6) and Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs), which are critical components that allow devices and networks to communicate across the internet.
The internet does not function without a well-organized system for assigning unique IP addresses and routing identifiers. RIRs ensure this process is fair, efficient, and consistent within their respective regions, preventing conflicts and promoting transparency in internet governance.
The Five Global RIRs
There are five officially recognized RIRs, each responsible for a specific part of the world:
AFRINIC – African Network Information Centre (Africa)
APNIC – Asia Pacific Network Information Centre (Asia Pacific)
ARIN – American Registry for Internet Numbers (Canada, the USA, parts of the Caribbean)
LACNIC – Latin America and Caribbean Network Information Centre (Latin America and the Caribbean)
RIPE NCC – Réseaux IP Européens Network Coordination Centre (Europe, Middle East, Central Asia)
Each RIR operates independently but collaborates on global policies and best practices through coordination bodies like the Number Resource Organization (NRO) and under guidance from IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority), a division of ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers).
Why Are RIRs Important?
RIRs perform several essential functions:
- IP Address Allocation: They distribute IP addresses to Internet Service Providers (ISPs), data centers, and other organizations.
- Policy Development: Through community consultation, RIRs facilitate the creation of rules for how internet number resources are managed and allocated.
- Database Maintenance: RIRs maintain public databases (WHOIS) that record who holds which IP addresses and ASNs, helping with internet troubleshooting and security.
- IPv6 Promotion: As IPv4 addresses become scarce, RIRs promote and support the adoption of IPv6.
- Education and Training: RIRs often provide training and resources to support the technical community and help stakeholders understand network best practices.
How Do RIRs Work with Other Internet Governance Bodies?
RIRs are part of the global internet governance ecosystem. They coordinate closely with:
- ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers): Oversees the global IP address space and domain names.
- IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority): Allocates large blocks of IP addresses and ASNs to RIRs.
- NIRs (National Internet Registries): In some regions, countries have their own national registries under the umbrella of an RIR.
RIRs are not regulatory bodies. Instead, they are community-focused, nonprofit organizations that emphasize bottom-up decision-making.
Conclusion
A Regional Internet Registry plays a crucial role in ensuring that IP addresses and routing identifiers are allocated efficiently, transparently, and in a way that supports the growth and stability of the internet. They form a bridge between global internet governance structures and local communities, making them vital players in how the internet works and evolves. Understanding the role of RIRs is key for anyone involved in networking, cybersecurity, or internet policy.
Trusted IPv4 Leasing for Business Growth
Get enterprise-grade IPv4 space quickly, with seamless deployment and end-to-end management.
Get Started with i.leaseRelated Blogs
Related Posts

Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses
The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they fear the perceived complexity or legal “gray areas.” As IPv4 exhaustion becomes a permanent reality, the value of these addresses has skyrocketed, yet misconceptions continue to stall potential transactions. At i.lease, powered by the real-world expertise of LARUS, we’ve seen how these myths prevent companies from unlocking significant capital.Read more Related Posts Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global Read more What happens when IP resources are mismanaged Poor IP resource management can lead to outages, security breaches, blacklisting, legal exposure and reputational damage across networks and business Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }

How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker
Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global transfers. IPv4 transactions are regulated transfers, not simple purchases — registries must approve documentation, justification and registration changes. Certified brokers reduce risk and delay by aligning buyers with registry policy, routing legitimacy and cross-region requirements. Why companies still need to buy IPv4 addresses The global supply of IPv4 addressesRead more Related Posts Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global Read more What happens when IP resources are mismanaged Poor IP resource management can lead to outages, security breaches, blacklisting, legal exposure and reputational damage across networks and business Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }

How to turn idle IPv4 addresses into a recurring revenue stream with iLease
Unlock the hidden value of unused IPv4 addresses with iLease, turning dormant digital infrastructure into a recurring revenue stream while navigating market demand, compliance and risk. Leasing idle IPv4 blocks can generate steady, long-term income without relinquishing ownership. Platforms like i.lease global IPv4 marketplace make it easier to monetise addresses and manage reputation and compliance. why IPv4 addresses still matter Despite the long-anticipated exhaustion of the IPv4 address space — aRead more Related Posts Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global Read more What happens when IP resources are mismanaged Poor IP resource management can lead to outages, security breaches, blacklisting, legal exposure and reputational damage across networks and business Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }