What is SSH? | Secure Shell (SSH) Protocol

Securing communications between devices is important, especially when managing remote systems. One of the most widely used and trusted protocols for secure remote access is SSH (Secure Shell). This article will dive into what SSH is, how it works, and why it’s so important for network security.
Table of Contents
What is SSH?
SSH (Secure Shell) is a network protocol that allows users to access and manage remote computers securely over an unsecured network, such as the Internet. SSH encrypts the communication between the client (your computer) and the remote server, ensuring that sensitive data like login credentials and commands cannot be intercepted by third parties.
It is a preferred method for system administrators, developers, and IT professionals to control remote servers and devices, providing a safer alternative to older protocols like Telnet, which send data in plain text.
How SSH Works
SSH operates using a client-server model, meaning a user connects from their local device (client) to a remote machine (server). Here’s how the process typically works:
Firstly, Establishing Connection: The user initiates a connection by using an SSH client (software) to communicate with the SSH server running on the remote machine.
Secondly, Authentication: The server authenticates the client using one of several methods, including password-based authentication or public key authentication. Once the authentication is successful, the user gains access to the server.
Thirdly, Encryption: During the session, all data transferred between the client and the server is encrypted, ensuring that even if someone intercepts the data, they cannot read or modify it.
Key Features of Secure Shell Protocols
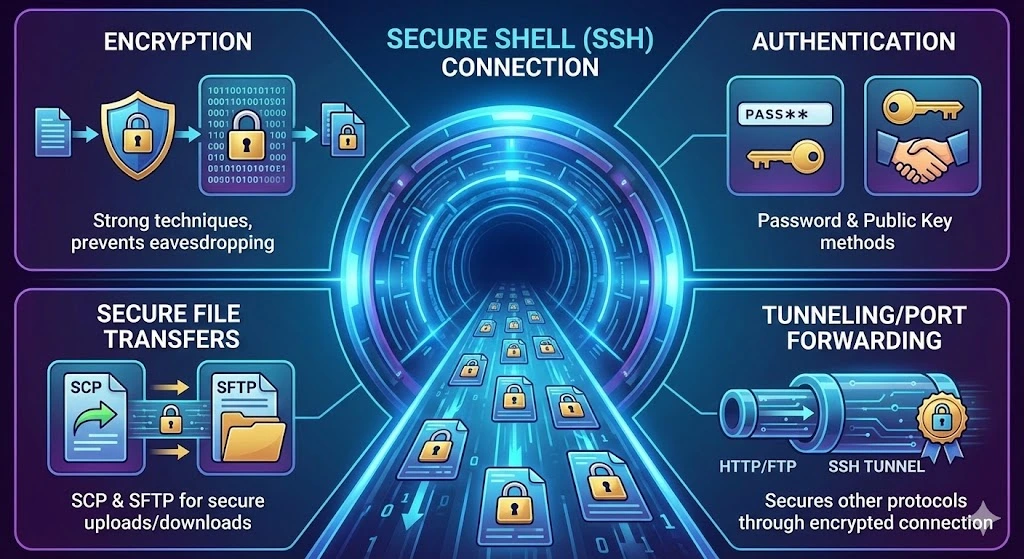
Encryption: SSH uses strong encryption techniques to ensure that all data exchanged between the client and the server is secure. This prevents eavesdropping and tampering by malicious actors.
Authentication: SSH supports several methods of authentication, including password authentication and public Key Authentication.
Secure File Transfers: SSH supports secure file transfers using protocols like SCP (Secure Copy) and SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol). This allows users to upload or download files to and from the remote server without worrying about security risks.
Tunneling/Port Forwarding: SSH can securely “tunnel” other protocols (such as HTTP or FTP) through the encrypted SSH connection, enabling secure communication for otherwise unsecured applications.
Common uses of SSH
SSH is primarily used for remote login, enabling system administrators and developers to access and manage remote machines anywhere securely. In addition, SSH is commonly used for file transfers, allowing users to securely move files between a local machine and a remote server using tools like SCP or SFTP.
Another important use of SSH is in automating tasks, such as deploying code, running scripts, or performing backups on remote systems. Additionally, SSH can be used for tunneling services, securely routing insecure network traffic through an encrypted connection to protect sensitive data.
Trusted IPv4 Leasing for Business Growth
Get enterprise-grade IPv4 space quickly, with seamless deployment and end-to-end management.
Get Started with i.leaseFAQs
What is the default port for SSH, and should I change it?
The default port for SSH is Port 22. It is highly recommended to change this default port to a custom number (e.g., 2222 or 1022) on your server. This simple security measure, known as “security through obscurity,” helps reduce the number of automated brute-force attacks and unauthorized login attempts from bots scanning for open default ports.
What is the difference between SSH and Telnet?
The main difference is security. Telnet transmits data, including usernames and passwords, in plain text, meaning anyone intercepting the network traffic can read the credentials. SSH (Secure Shell) uses encryption to scramble data during transmission, making it unreadable to hackers. SSH effectively replaced Telnet for this reason.
Is SSH the same as a VPN?
No, they serve different purposes. SSH is primarily used to securely access and manage a specific remote computer or server via a command line. A VPN (Virtual Private Network) encrypts the internet traffic for an entire device or network, effectively masking your location and securing all browser and app activity. However, SSH tunneling can mimic some VPN features by routing traffic through a secure server.
Can SSH be used on Windows?
Yes. While SSH is native to Linux and macOS terminals, Windows users can use SSH via Windows PowerShell, the Command Prompt (in newer versions of Windows 10/11), or by using third-party clients like PuTTY or MobaXterm.
Related Posts

Inbound vs. Outbound IPv4 Leasing: A Complete Guide for Enterprises
Understanding IPv4 leasing helps enterprises manage scarce address space, reducing risk and unlocking strategic growth opportunities in today’s digital economy. Key points Distinguishes between inbound (leasing in) and outbound (leasing out) IPv4 approaches and their strategic implications. Highlights contract structures, registry risk management and continuity considerations affecting global number resources. Inbound vs. outbound IPv4 leasing: complete enterprise guide In the post-exhaustion era of Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4),Read more Related Posts Inbound vs. Outbound IPv4 Leasing: A Complete Guide for Enterprises Understanding IPv4 leasing helps enterprises manage scarce address space, reducing risk and unlocking strategic growth opportunities in today’s digital economy. Key Read more Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to turn idle IPv4 addresses into a recurring revenue stream with iLease Unlock the hidden value of unused IPv4 addresses with iLease, turning dormant digital infrastructure into a recurring revenue stream while Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }

Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses
The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they fear the perceived complexity or legal “gray areas.” As IPv4 exhaustion becomes a permanent reality, the value of these addresses has skyrocketed, yet misconceptions continue to stall potential transactions. At i.lease, powered by the real-world expertise of LARUS, we’ve seen how these myths prevent companies from unlocking significant capital.Read more Related Posts Inbound vs. Outbound IPv4 Leasing: A Complete Guide for Enterprises Understanding IPv4 leasing helps enterprises manage scarce address space, reducing risk and unlocking strategic growth opportunities in today’s digital economy. Key Read more Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to turn idle IPv4 addresses into a recurring revenue stream with iLease Unlock the hidden value of unused IPv4 addresses with iLease, turning dormant digital infrastructure into a recurring revenue stream while Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }

How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker
Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global transfers. IPv4 transactions are regulated transfers, not simple purchases — registries must approve documentation, justification and registration changes. Certified brokers reduce risk and delay by aligning buyers with registry policy, routing legitimacy and cross-region requirements. Why companies still need to buy IPv4 addresses The global supply of IPv4 addressesRead more Related Posts Inbound vs. Outbound IPv4 Leasing: A Complete Guide for Enterprises Understanding IPv4 leasing helps enterprises manage scarce address space, reducing risk and unlocking strategic growth opportunities in today’s digital economy. Key Read more Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to turn idle IPv4 addresses into a recurring revenue stream with iLease Unlock the hidden value of unused IPv4 addresses with iLease, turning dormant digital infrastructure into a recurring revenue stream while Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }