What is a Proxy IP?
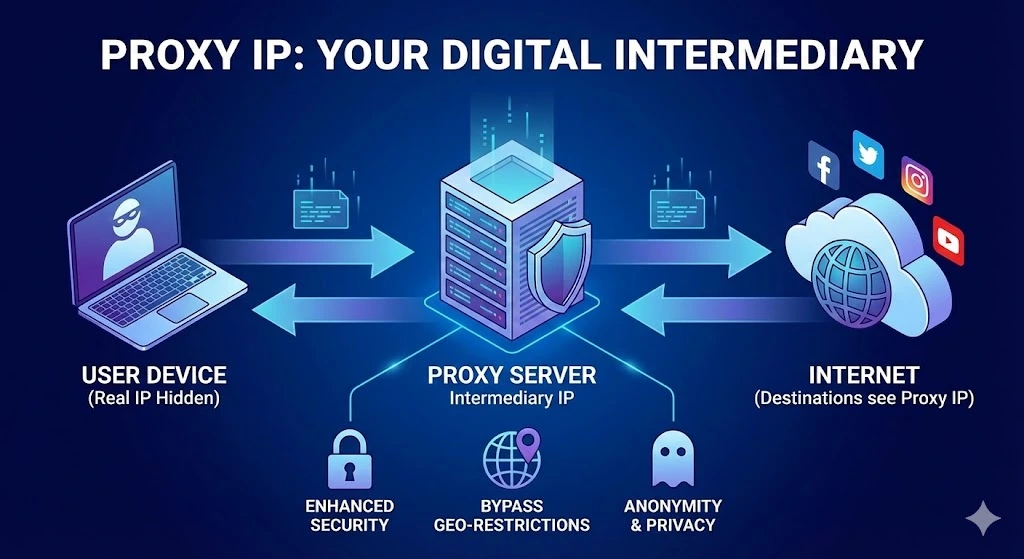
A proxy IP is an intermediary IP address used to mask or relay your original IP address when accessing the Internet. It acts as a gateway between the user and the web. When a request is made to access a website, the proxy server (which uses the proxy IP) forwards that request, hiding the user’s real IP address from the website. This allows for increased privacy and anonymity when browsing online.
Table of Contents
How Proxy IP Works
When you use a proxy, your device sends a request to the proxy server, which forwards it to the target website. The website then sees the request as coming from the proxy server, not your IP. This shields your original identity and location from the website. Afterward, the website’s response is returned to the proxy server, which forwards it to you.
Types of Proxy IPs
HTTP Proxies: These only work for web pages and are great for browsing.
SOCKS Proxies: They handle a wider range of traffic, including emails, torrent files, and FTP.
Transparent Proxies: These identify themselves and pass the original IP address, often used in caching.
Anonymous Proxies: These hide the user’s IP address but identify themselves as proxies.
High Anonymity Proxies: These provide maximum privacy by not identifying themselves as proxies and completely hiding the user’s IP.
Key Functions and Use Cases
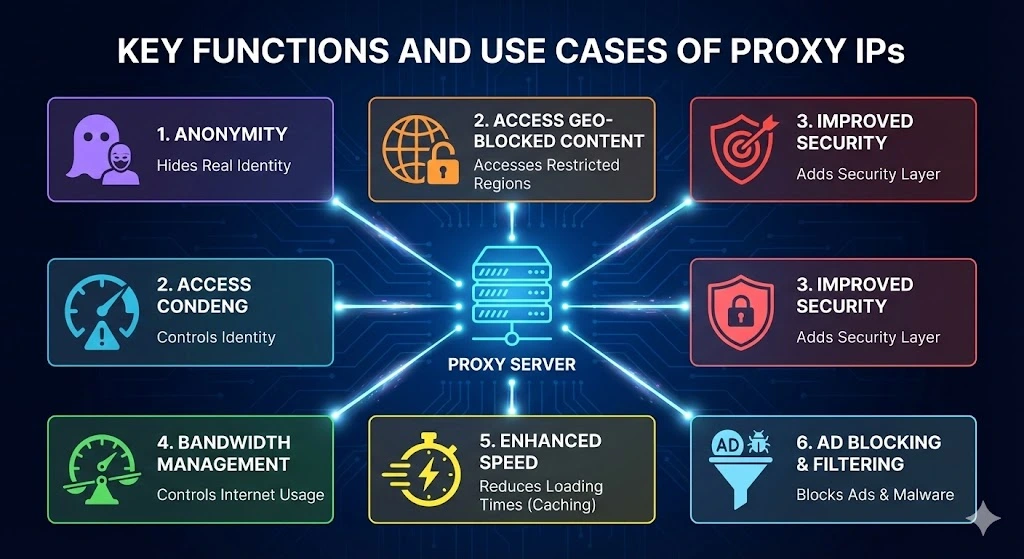
1. Anonymity: Proxy IPs hide your real identity online, allowing you to browse the web without revealing personal information.
2. Access Geo-Blocked Content: Proxies enable users to access content that is restricted in certain regions by assigning IPs from specific locations.
3. Improved Security: By masking the original IP address, proxy servers add a layer of security, making it harder for hackers to target the user directly.
4. Bandwidth Management: Proxies can help organizations manage and control internet bandwidth usage, preventing congestion.
5. Enhanced Speed: Certain proxies can cache web pages, reducing loading times for frequently accessed websites.
6. Ad Blocking and Filtering: Proxy servers can block ads, malware, or filter content to ensure a safer browsing experience.
Common Use Cases for Proxy IPs
1. Businesses: Companies use proxies for security, load balancing, and to prevent unauthorized access to their internal systems.
2. SEO and Marketing: Marketers use proxies to gather competitor data or analyze web traffic from different locations.
3. Streaming: Users rely on proxy IPs to bypass geo-restrictions and access content not available in their regions.
4. Privacy Enthusiasts: Those concerned with online privacy use proxy IPs to hide their real IP address while browsing.
The Difference Between Proxy and VPN
While both proxies and VPNs hide your IP address, a VPN encrypts all your internet traffic, offering a more secure connection. Proxies generally do not encrypt data, but they can be faster than VPNs for some use cases since they don’t handle heavy encryption.
Final Thoughts
Proxy IPs are essential tools for maintaining privacy, accessing restricted content, and improving online security. Whether for personal use, business operations, or marketing analysis, proxies offer a flexible solution to interact with the web more effectively. Some of the most popular proxy providers include Luminati, Smartproxy, and Bright Data, offering a range of services tailored to different needs.
Trusted IPv4 Leasing for Business Growth
Get enterprise-grade IPv4 space quickly, with seamless deployment and end-to-end management.
Get Started with i.leaseRelated Posts

Inbound vs. Outbound IPv4 Leasing: A Complete Guide for Enterprises
Understanding IPv4 leasing helps enterprises manage scarce address space, reducing risk and unlocking strategic growth opportunities in today’s digital economy. Key points Distinguishes between inbound (leasing in) and outbound (leasing out) IPv4 approaches and their strategic implications. Highlights contract structures, registry risk management and continuity considerations affecting global number resources. Inbound vs. outbound IPv4 leasing: complete enterprise guide In the post-exhaustion era of Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4),Read more Related Posts Inbound vs. Outbound IPv4 Leasing: A Complete Guide for Enterprises Understanding IPv4 leasing helps enterprises manage scarce address space, reducing risk and unlocking strategic growth opportunities in today’s digital economy. Key Read more Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to turn idle IPv4 addresses into a recurring revenue stream with iLease Unlock the hidden value of unused IPv4 addresses with iLease, turning dormant digital infrastructure into a recurring revenue stream while Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }

Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses
The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they fear the perceived complexity or legal “gray areas.” As IPv4 exhaustion becomes a permanent reality, the value of these addresses has skyrocketed, yet misconceptions continue to stall potential transactions. At i.lease, powered by the real-world expertise of LARUS, we’ve seen how these myths prevent companies from unlocking significant capital.Read more Related Posts Inbound vs. Outbound IPv4 Leasing: A Complete Guide for Enterprises Understanding IPv4 leasing helps enterprises manage scarce address space, reducing risk and unlocking strategic growth opportunities in today’s digital economy. Key Read more Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to turn idle IPv4 addresses into a recurring revenue stream with iLease Unlock the hidden value of unused IPv4 addresses with iLease, turning dormant digital infrastructure into a recurring revenue stream while Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }

How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker
Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global transfers. IPv4 transactions are regulated transfers, not simple purchases — registries must approve documentation, justification and registration changes. Certified brokers reduce risk and delay by aligning buyers with registry policy, routing legitimacy and cross-region requirements. Why companies still need to buy IPv4 addresses The global supply of IPv4 addressesRead more Related Posts Inbound vs. Outbound IPv4 Leasing: A Complete Guide for Enterprises Understanding IPv4 leasing helps enterprises manage scarce address space, reducing risk and unlocking strategic growth opportunities in today’s digital economy. Key Read more Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to turn idle IPv4 addresses into a recurring revenue stream with iLease Unlock the hidden value of unused IPv4 addresses with iLease, turning dormant digital infrastructure into a recurring revenue stream while Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }