What is IP Subnetting? A Comprehensive Introduction

Understanding IP subnetting is essential for designing efficient and scalable networks. Subnetting allows network administrators to divide a single IP address range into smaller, more manageable subnetworks, enabling better organization of network resources and efficient allocation of IP addresses. In this article, we’ll provide a comprehensive introduction to IP subnetting, covering its fundamental concepts, benefits, and practical applications.
Table of Contents
Before we delve into subnetting, let’s review the basics of IP addresses.
Understanding IP Addresses
An IP address is a unique numerical identifier assigned to each device connected to a network. IPv4 addresses, the most commonly used type of IP address, consist of four sets of numbers separated by dots (e.g., 192.168.1.1). Each set of numbers ranges from 0 to 255, representing different portions of the address.
Now, let’s proceed to our main topic: subnetting.
What is subnetting?
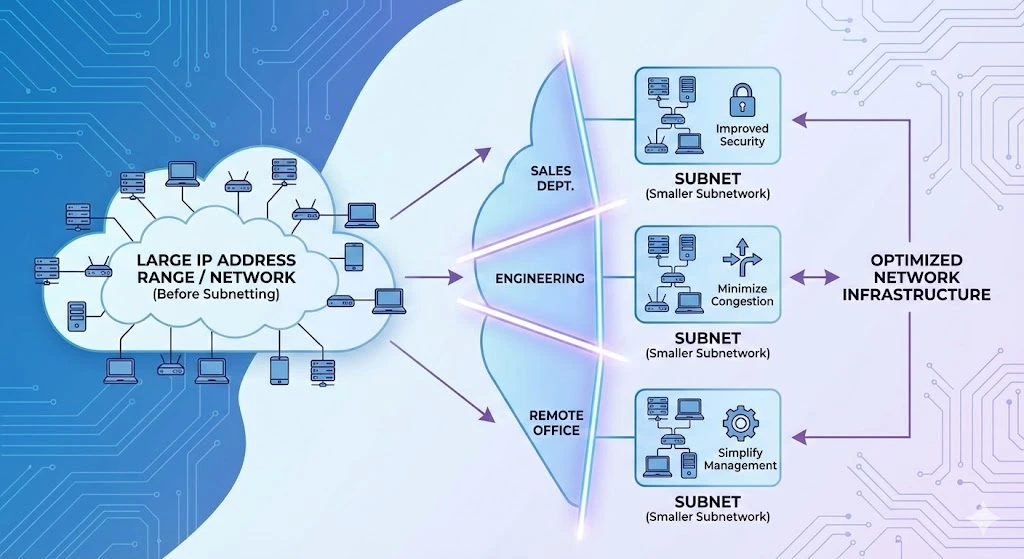
Subnetting is the process of dividing a large IP address range, or network, into smaller, more manageable subnetworks, or subnets. This allows organizations to optimize their network infrastructure by segmenting devices into logical groups based on factors such as location, function, or department. Subnetting helps minimize network congestion, improve security, and simplify network management tasks.
Each RIR has its own nuances. Such as whilst AFRINIC prevents transfers to intra-RIR only, APNIC, ARIN, RIPE, and LACNIC all facilitate inter-RIR transfers under reciprocal, needs-based policies. The registry affirms the fact the seller is the legitimate owner of the IP addresses and makes sure that all applicable regulations are met before RIR-led transfers can take position. Each transfer involves documentation, justification of need, and processing fees, making the process thorough but sometimes slow.
Benefits of Subnetting
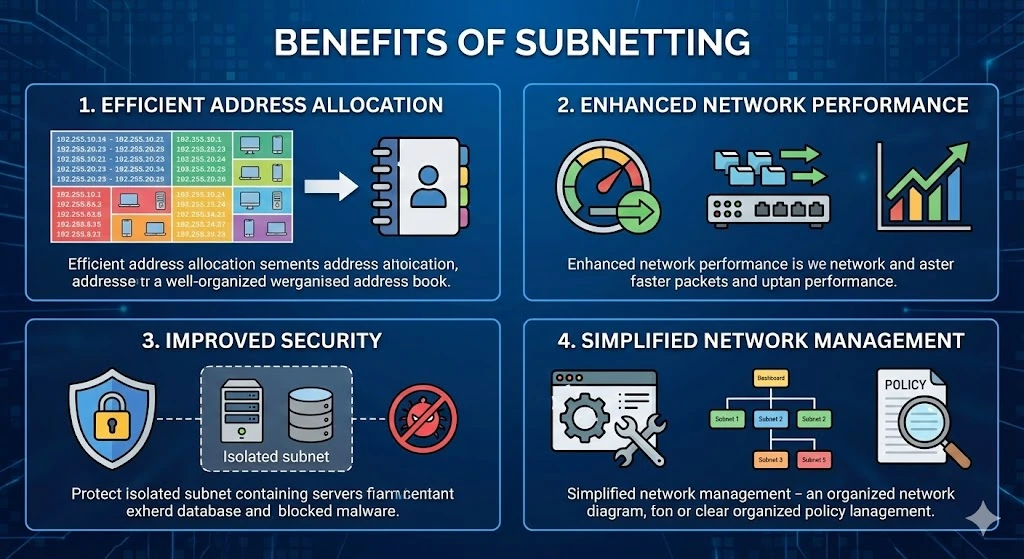
1. Efficient Address Allocation
Subnetting enables organizations to allocate IP addresses more efficiently by dividing a large address space into smaller, more targeted subnets. This reduces IP address waste and ensures that each device receives an appropriate address within its subnet.
2. Enhanced Network Performance
By reducing the size of broadcast domains and segmenting traffic into smaller subnets, subnetting helps minimize network congestion and improve overall network performance. This allows for faster data transmission and better bandwidth utilization.
3. Improved Security
Subnetting enhances network security by isolating sensitive or critical network resources within their own subnets. This limits the scope of potential security breaches and helps contain network threats, such as malware or unauthorized access attempts.
4. Simplified Network Management
Subnetting simplifies network management tasks by organizing devices into logical groups based on their subnet assignments. This makes it easier to configure and troubleshoot network devices, track IP address usage, and implement network policies and rules.
Key Concepts in Subnetting
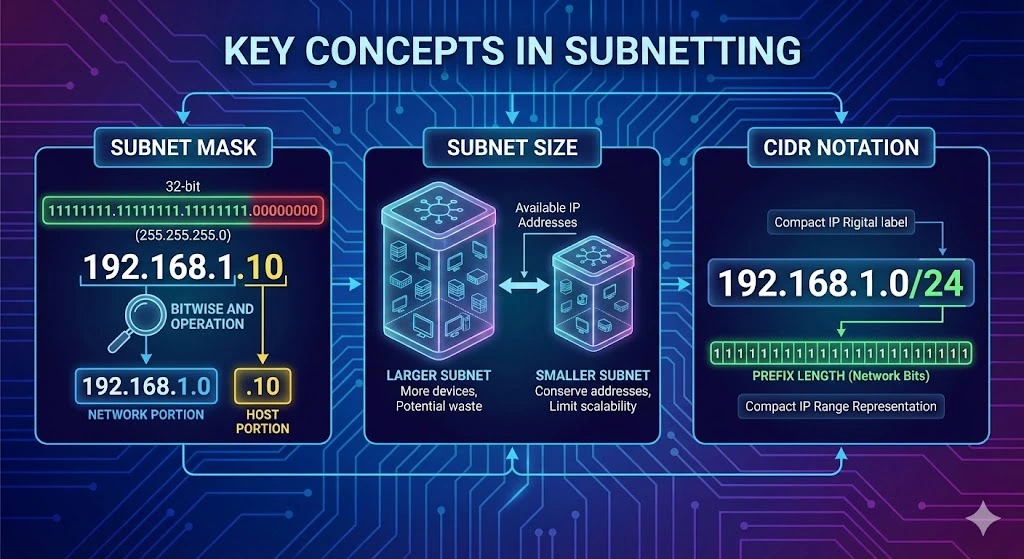
Subnet Mask: A subnet mask is a 32-bit binary number that defines the boundaries of a subnet within an IP address range. It consists of a series of consecutive binary 1s, followed by a series of consecutive binary 0s. The subnet mask is applied to an IP address using a bitwise AND operation to determine the network and host portions of the address.
Subnet Size: The size of a subnet is determined by the number of available IP addresses within the subnet range. Larger subnets accommodate more devices but may lead to greater address waste, while smaller subnets conserve addresses but may limit scalability.
CIDR Notation: The Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) notation is a compact representation of IP address ranges that includes the network address and subnet mask. CIDR notation uses a forward slash followed by a number to indicate the number of bits in the subnet mask (e.g., 192.168.1.0/24).
Practical Applications of Subnetting
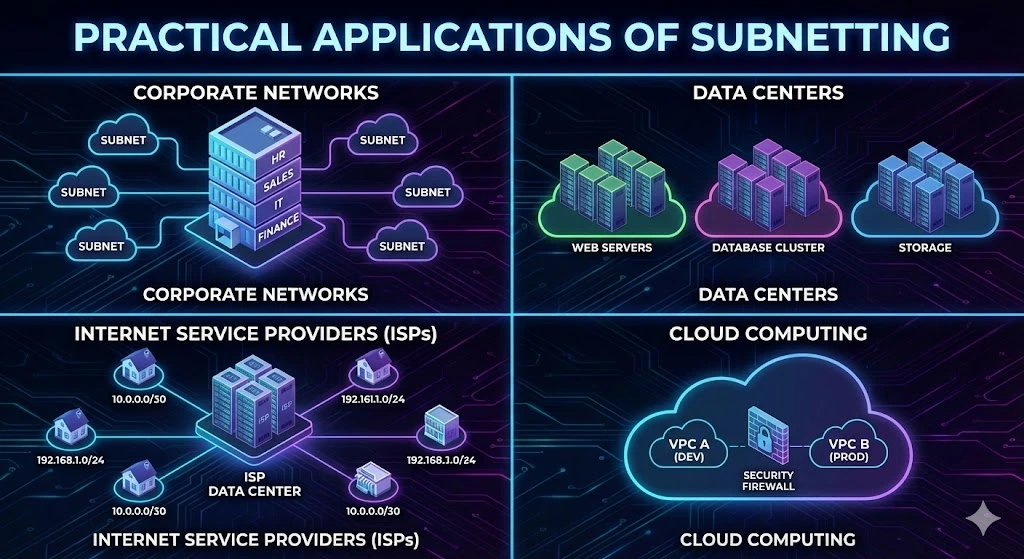
Corporate Networks: Subnetting is commonly used in corporate networks to divide large address ranges into smaller subnets for different departments, floors, or locations. This improves network performance, enhances security, and simplifies network management.
Internet Service Providers (ISPs): ISPs use subnetting to allocate IP address ranges to their customers more efficiently. By subnetting their address space, ISPs can accommodate more customers and reduce IP address waste.
Data Centers: In data center environments, subnetting helps organize servers and network devices into logical groups based on their roles or functions. This facilitates efficient resource allocation, load balancing, and fault tolerance.
Cloud Computing: Subnetting is essential in cloud computing environments for creating virtual private networks (VPNs), isolating workloads, and enforcing network security policies. Subnetting allows cloud providers to partition their infrastructure and offer customized networking solutions to customers.
IP Subnetting in a brief
In a nutshell, IP subnetting is a fundamental concept in networking that plays a crucial role in optimizing network infrastructure, enhancing security, and simplifying network management. By understanding the principles of subnetting and its practical applications, network administrators can design scalable, efficient, and resilient networks that meet the evolving needs of their organizations. Whether you’re configuring a small office network or managing a large-scale data center, mastering IP subnetting is essential for building robust and reliable network environments.
Are you interested in learning more about IP addresses? or do you want to lease an IP address? Contact us now!
Trusted IPv4 Leasing for Business Growth
Get enterprise-grade IPv4 space quickly, with seamless deployment and end-to-end management.
Get Started with i.leaseFAQs
How many usable IP addresses are in a /24 subnet?
A /24 subnet has 254 usable IP addresses. While there are 256 total addresses in the range (2^8), two are always reserved: the Network Address (the first IP) and the Broadcast Address (the last IP).
What is CIDR notation and how does it work?
CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) notation is a shorthand way to show an IP address and its associated subnet mask. The number after the slash (e.g., /24) represents the number of “bits” dedicated to the network portion of the address. The higher the number after the slash, the smaller the number of available host IPs in that subnet.
Why is 192.168.1.1 the most common IP address?
This address belongs to a “Private” IP range designated for local networks. Most router manufacturers set 192.168.1.1 as the default gateway (the “front door” to the internet) for home and small business routers because it is easy to remember and complies with standard IPv4 subnetting rules.
Related Posts

Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses
The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they fear the perceived complexity or legal “gray areas.” As IPv4 exhaustion becomes a permanent reality, the value of these addresses has skyrocketed, yet misconceptions continue to stall potential transactions. At i.lease, powered by the real-world expertise of LARUS, we’ve seen how these myths prevent companies from unlocking significant capital.Read more Related Posts Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global Read more What happens when IP resources are mismanaged Poor IP resource management can lead to outages, security breaches, blacklisting, legal exposure and reputational damage across networks and business Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }

How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker
Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global transfers. IPv4 transactions are regulated transfers, not simple purchases — registries must approve documentation, justification and registration changes. Certified brokers reduce risk and delay by aligning buyers with registry policy, routing legitimacy and cross-region requirements. Why companies still need to buy IPv4 addresses The global supply of IPv4 addressesRead more Related Posts Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global Read more What happens when IP resources are mismanaged Poor IP resource management can lead to outages, security breaches, blacklisting, legal exposure and reputational damage across networks and business Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }

How to turn idle IPv4 addresses into a recurring revenue stream with iLease
Unlock the hidden value of unused IPv4 addresses with iLease, turning dormant digital infrastructure into a recurring revenue stream while navigating market demand, compliance and risk. Leasing idle IPv4 blocks can generate steady, long-term income without relinquishing ownership. Platforms like i.lease global IPv4 marketplace make it easier to monetise addresses and manage reputation and compliance. why IPv4 addresses still matter Despite the long-anticipated exhaustion of the IPv4 address space — aRead more Related Posts Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global Read more What happens when IP resources are mismanaged Poor IP resource management can lead to outages, security breaches, blacklisting, legal exposure and reputational damage across networks and business Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }