IP Address Marketplace Comprehensive Guide

IP addresses are crucial for identifying devices and enabling communication across networks. As the internet continues to expand, the demand for IP addresses has surged, leading to the rise of the IP address marketplace. This unique market allows businesses and individuals to buy, sell, or lease IP addresses, ensuring that resources are optimally utilized in a world where IPv4 addresses are becoming scarce.
Table of Contents
What Is an IP Address Marketplace?
An IP address marketplace is a platform where organizations and individuals can trade IP address blocks. This marketplace has emerged due to the limited availability of IPv4 addresses. The exhaustion of these addresses has created a supply-demand imbalance, making them valuable digital assets. The marketplace facilitates the transfer of unused or underutilized IPv4 addresses from companies that no longer need them to those that do.
Why Do IP Address Marketplaces Exist?
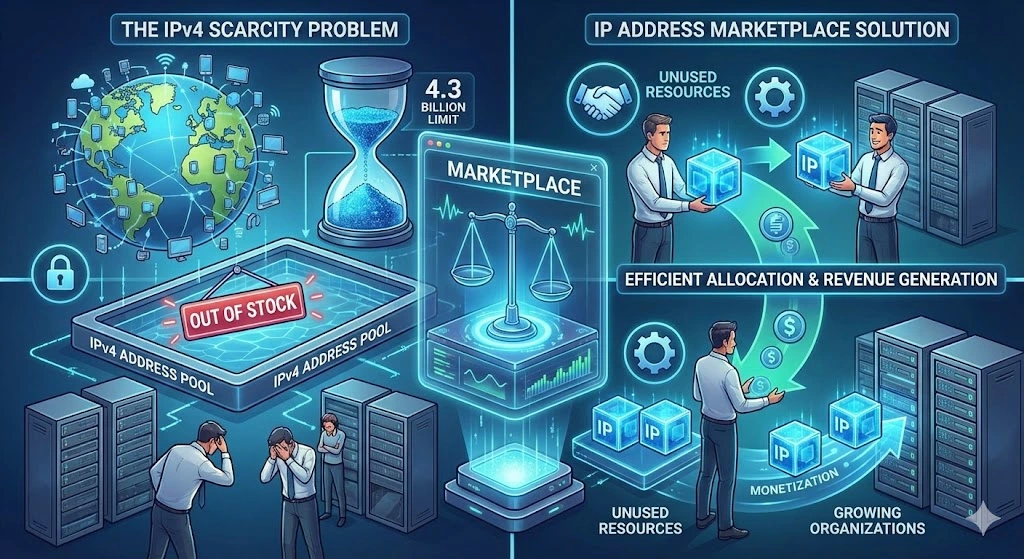
The IP address marketplace was born out of necessity when IPv4 addresses, limited to approximately 4.3 billion unique addresses, began running out. As more devices connected to the Internet, organizations found it increasingly difficult to obtain new addresses. Meanwhile, some entities held large blocks of unused IP addresses, creating an opportunity for monetization.
This market solves several challenges:
1. Scarcity of IPv4 addresses: With only a finite number of IPv4 addresses, many organizations need to purchase blocks for their operations.
2. Efficient use of resources: IP address marketplaces promote the efficient allocation of addresses by allowing businesses to sell or lease unused IP addresses.
3. Monetization: Companies that own unused IP addresses can generate revenue by selling or leasing them.
How Does an IP Address Marketplace Work?
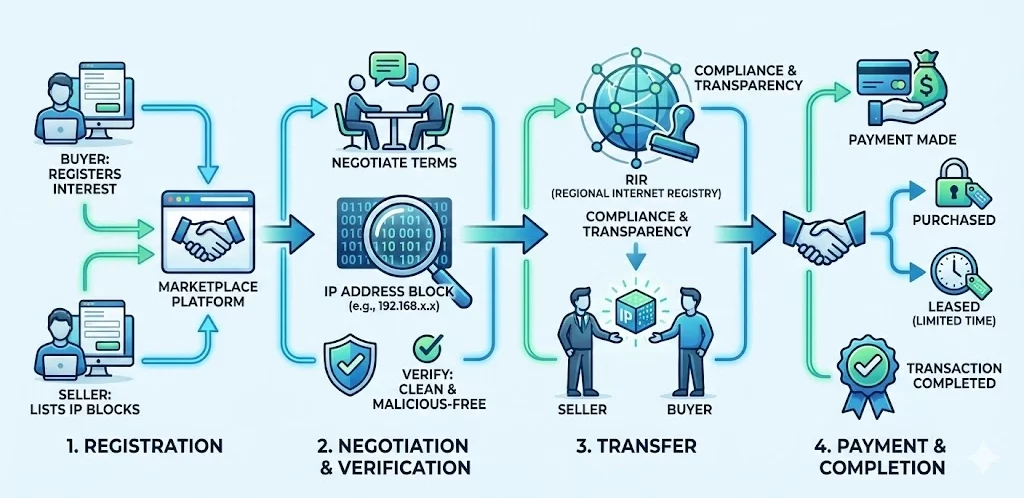
In an IP address marketplace, buyers and sellers engage in transactions to trade blocks of IP addresses, typically under the supervision of an IP address broker or through a specialized platform. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how the marketplace works:
Registration: Both buyers and sellers must register on the marketplace platform. Sellers list available IP address blocks, while buyers express their interest in acquiring them.
Negotiation and Verification: Once a buyer is interested, they negotiate with the seller. The marketplace or a third-party broker often verifies the IP addresses, ensuring they are clean and have no associated malicious activities.
Transfer: After an agreement is reached, the seller transfers the ownership of the IP addresses to the buyer. The transaction is usually carried out through the Regional Internet Registry (RIR) for transparency and compliance.
Payment and Completion: The buyer makes the payment, and the transaction is completed. Some marketplaces offer leasing options, allowing buyers to use the IP addresses for a limited time instead of purchasing them outright.
IP Address Marketplaces
As the Internet continues to grow and IPv4 addresses become even scarcer, the IP address marketplace will play an increasingly critical role in the digital ecosystem. The rise of IPv6—the next-generation IP address protocol—will eventually mitigate the shortage, but the transition is slow, and IPv4 will continue to be relevant for many years to come.
In the meantime, IP address marketplaces will thrive, facilitating the exchange of these valuable digital assets. Companies and individuals seeking to expand their digital infrastructure or monetize their unused IP blocks will continue to turn to these marketplaces for solutions.
Trusted IPv4 Leasing for Business Growth
Get enterprise-grade IPv4 space quickly, with seamless deployment and end-to-end management.
Get Started with i.leaseRelated Posts

Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses
The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they fear the perceived complexity or legal “gray areas.” As IPv4 exhaustion becomes a permanent reality, the value of these addresses has skyrocketed, yet misconceptions continue to stall potential transactions. At i.lease, powered by the real-world expertise of LARUS, we’ve seen how these myths prevent companies from unlocking significant capital.Read more Related Posts Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global Read more What happens when IP resources are mismanaged Poor IP resource management can lead to outages, security breaches, blacklisting, legal exposure and reputational damage across networks and business Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }

How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker
Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global transfers. IPv4 transactions are regulated transfers, not simple purchases — registries must approve documentation, justification and registration changes. Certified brokers reduce risk and delay by aligning buyers with registry policy, routing legitimacy and cross-region requirements. Why companies still need to buy IPv4 addresses The global supply of IPv4 addressesRead more Related Posts Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global Read more What happens when IP resources are mismanaged Poor IP resource management can lead to outages, security breaches, blacklisting, legal exposure and reputational damage across networks and business Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }

How to turn idle IPv4 addresses into a recurring revenue stream with iLease
Unlock the hidden value of unused IPv4 addresses with iLease, turning dormant digital infrastructure into a recurring revenue stream while navigating market demand, compliance and risk. Leasing idle IPv4 blocks can generate steady, long-term income without relinquishing ownership. Platforms like i.lease global IPv4 marketplace make it easier to monetise addresses and manage reputation and compliance. why IPv4 addresses still matter Despite the long-anticipated exhaustion of the IPv4 address space — aRead more Related Posts Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global Read more What happens when IP resources are mismanaged Poor IP resource management can lead to outages, security breaches, blacklisting, legal exposure and reputational damage across networks and business Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }