Internet Censorship and the Great Firewall
Internet Censorship and the Great Firewall: Understanding the Boundaries of the Digital World
The Internet has revolutionized the way we connect, learn, and share information, but its open nature has also led to significant debates about control, privacy, and freedom.
Table of Contents
At the center of these discussions lies the concept of Internet censorship and, most notably, China’s Great Firewall (GFW). This article explores the intricacies of Internet censorship, its implementation, and the technology behind the Great Firewall.
What Is Internet Censorship?
Internet censorship refers to the control or suppression of access to information on the Internet. Governments, private organizations, or other regulatory bodies may enforce censorship to restrict the content available to users. This can range from blocking specific websites to filtering search results or monitoring online activities.
Why Is Internet Censorship Implemented?
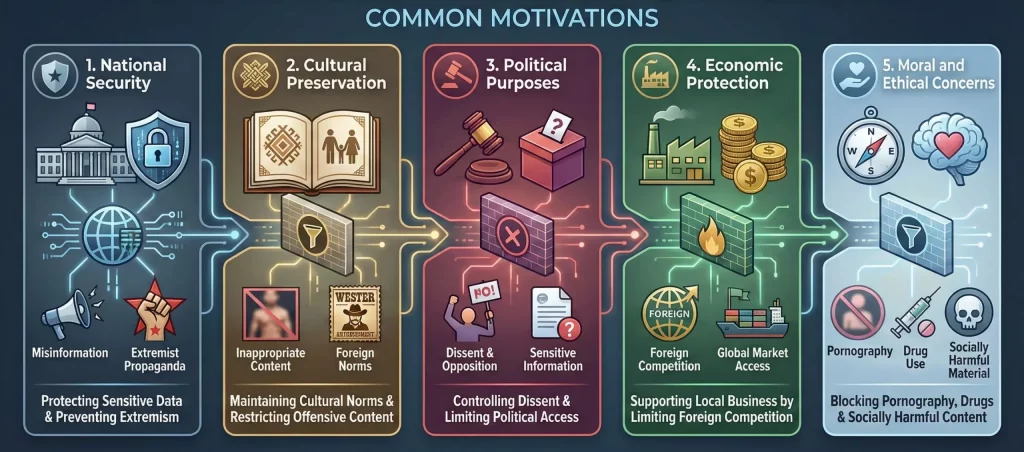
The reasons for implementing Internet censorship vary by country, ideology, and circumstance. Common motivations include:
1) National Security: Protecting sensitive government data and preventing the spread of misinformation or extremist propaganda.
2) Cultural Preservation: Maintaining cultural norms by restricting access to inappropriate or offensive content.
3) Political Purposes: Controlling dissent and opposition by limiting access to politically sensitive information.
4) Economic Protection: Supporting local businesses by limiting competition from foreign companies.
5) Moral and Ethical Concerns: Blocking content related to pornography, drug use, or other socially harmful material.
While proponents argue that censorship is essential for maintaining societal order, critics view it as a violation of free speech and access to information.
What Is the Great Firewall?
The Great Firewall, officially known as the “Golden Shield Project,” is China’s sophisticated Internet censorship system. Implemented in the early 2000s, the Great Firewall is designed to regulate the flow of information and control access to international websites and services that conflict with the government’s policies and ideologies.
Key features of the Great Firewall include:
- Blocking access to popular websites like Google, Facebook, and Twitter.
- Restricting foreign news outlets and platforms critical of the Chinese government.
- Monitoring and filtering user activities to ensure compliance with local laws.
How Is Internet Censorship Implemented?
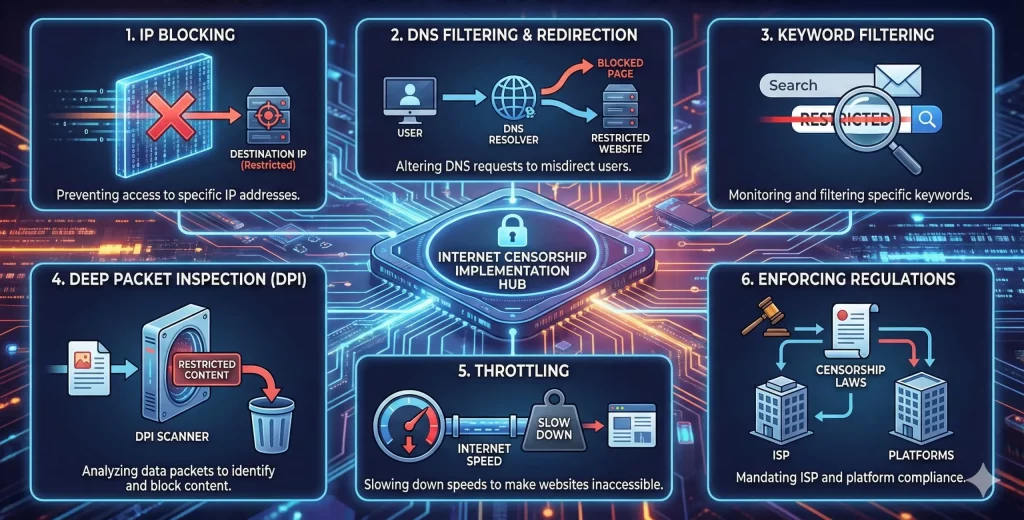
Internet censorship involves a combination of technical measures and regulatory policies. Here are the primary methods:
- IP Blocking: Preventing access to specific IP addresses linked to restricted websites.
- DNS Filtering and Redirection: Altering Domain Name System (DNS) requests to misdirect users trying to reach restricted websites.
- Keyword Filtering: Monitoring and filtering specific keywords in search queries, emails, or social media posts.
- Deep Packet Inspection (DPI): Analyzing data packets to identify and block restricted content.
- Throttling: Slowing down Internet speeds for certain websites or services to make them virtually inaccessible.
- Enforcing Regulations: Mandating that Internet service providers (ISPs) and platforms comply with censorship laws.
How Does the Great Firewall Work?
The Great Firewall employs an advanced blend of the above techniques, enhanced by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning technologies. Here’s how it functions:
- Network Surveillance: The Chinese government monitors traffic through DPI, allowing authorities to block or throttle connections to restricted websites.
- URL Filtering: Specific URLs or domains are blacklisted to prevent users from accessing them.
- Keyword Monitoring: Content with sensitive keywords is flagged and blocked, affecting search engines and social media platforms.
- VPN Detection and Blocking: Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), often used to bypass censorship, are detected and disabled through advanced algorithms.
- Collaboration with Local Companies: Domestic platforms like WeChat and Baidu operate under strict regulatory guidelines to enforce censorship internally.
Conclusion
Internet censorship and the Great Firewall exemplify the complexities of regulating the digital space. While censorship aims to achieve goals like national security and cultural preservation, it often raises ethical questions about freedom of expression and access to information.
The Great Firewall, in particular, showcases how technology can be leveraged to control online narratives, creating a heavily monitored and filtered Internet ecosystem.
Trusted IPv4 Leasing for Business Growth
Get enterprise-grade IPv4 space quickly, with seamless deployment and end-to-end management.
Get Started with i.leaseRelated Posts

Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses
The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they fear the perceived complexity or legal “gray areas.” As IPv4 exhaustion becomes a permanent reality, the value of these addresses has skyrocketed, yet misconceptions continue to stall potential transactions. At i.lease, powered by the real-world expertise of LARUS, we’ve seen how these myths prevent companies from unlocking significant capital.Read more Related Posts Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global Read more What happens when IP resources are mismanaged Poor IP resource management can lead to outages, security breaches, blacklisting, legal exposure and reputational damage across networks and business Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }

How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker
Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global transfers. IPv4 transactions are regulated transfers, not simple purchases — registries must approve documentation, justification and registration changes. Certified brokers reduce risk and delay by aligning buyers with registry policy, routing legitimacy and cross-region requirements. Why companies still need to buy IPv4 addresses The global supply of IPv4 addressesRead more Related Posts Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global Read more What happens when IP resources are mismanaged Poor IP resource management can lead to outages, security breaches, blacklisting, legal exposure and reputational damage across networks and business Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }

How to turn idle IPv4 addresses into a recurring revenue stream with iLease
Unlock the hidden value of unused IPv4 addresses with iLease, turning dormant digital infrastructure into a recurring revenue stream while navigating market demand, compliance and risk. Leasing idle IPv4 blocks can generate steady, long-term income without relinquishing ownership. Platforms like i.lease global IPv4 marketplace make it easier to monetise addresses and manage reputation and compliance. why IPv4 addresses still matter Despite the long-anticipated exhaustion of the IPv4 address space — aRead more Related Posts Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global Read more What happens when IP resources are mismanaged Poor IP resource management can lead to outages, security breaches, blacklisting, legal exposure and reputational damage across networks and business Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }