Dynamic vs. Static IP Addresses
In the realm of networking, IP addresses serve as the backbone of communication, facilitating the exchange of data packets across the internet and local networks. When it comes to assigning IP addresses to devices, businesses often have to choose between dynamic and static IP addresses. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the differences between dynamic and static IP addresses, explore their respective advantages and disadvantages, and help you make an informed decision for your business needs.
Table of Contents
Understanding Dynamic IP Addresses
Dynamic IP addresses are assigned to devices by a DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server dynamically. Each time a device connects to the network, the DHCP server assigns it a temporary IP address from a pool of available addresses. These IP addresses are subject to change each time the device reconnects to the network or when the DHCP lease expires.
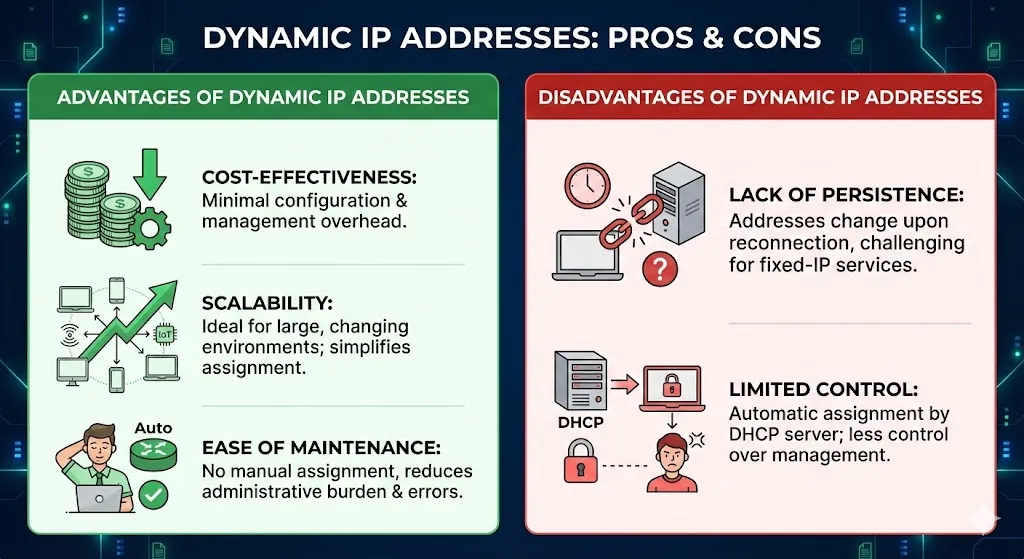
Advantages of Dynamic IP Addresses
- Cost-Effectiveness: Dynamic IP addresses are typically more cost-effective for businesses as they require minimal configuration and management overhead.
- Scalability: Dynamic IP addressing is well-suited for environments with a large number of devices or frequent changes in network topology, as it simplifies the process of assigning and managing IP addresses.
- Ease of Maintenance: With dynamic IP addressing, businesses don’t have to manually assign or configure IP addresses for individual devices, reducing administrative burden and potential errors.
Disadvantages of Dynamic IP Addresses
- Lack of Persistence: Dynamic IP addresses can change each time a device reconnects to the network, making it challenging to maintain consistent connections for services that rely on fixed IP addresses.
- Limited Control: Businesses have limited control over the assignment and management of dynamic IP addresses, as they are automatically assigned by the DHCP server based on availability.
Understanding Static IP Addresses
Static IP addresses, on the other hand, are manually configured and remain constant for each device. Unlike dynamic IP addresses, static IP addresses do not change over time unless manually reconfigured by a network administrator. Static IP addresses are typically used for devices that require permanent, fixed addresses, such as servers, printers, and network appliances.
Advantages of Dynamic IP Addresses
- Cost-Effectiveness: Dynamic IP addresses are typically more cost-effective for businesses as they require minimal configuration and management overhead.
- Scalability: Dynamic IP addressing is well-suited for environments with a large number of devices or frequent changes in network topology, as it simplifies the process of assigning and managing IP addresses.
- Ease of Maintenance: With dynamic IP addressing, businesses don’t have to manually assign or configure IP addresses for individual devices, reducing administrative burden and potential errors.
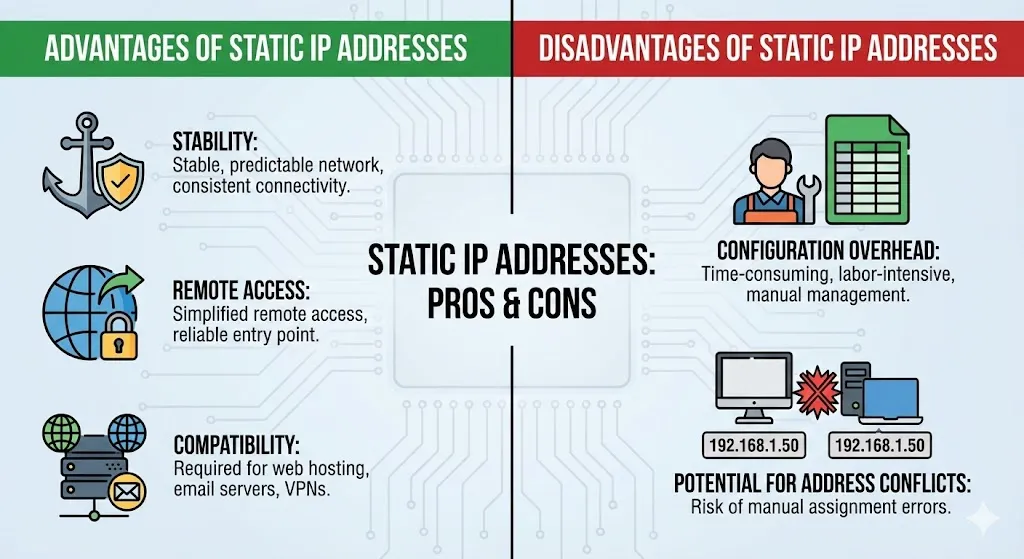
Advantages of static IP addresses
- Stability: Static IP addresses provide a stable and predictable network environment, ensuring consistent connectivity for devices that require fixed addresses.
- Remote Access: Static IP addresses simplify remote access to devices, services, and applications, as they provide a reliable point of entry into the network.
- Compatibility: Some applications and services, such as web hosting, email servers, and virtual private networks (VPNs), require static IP addresses for proper functionality and security.
Disadvantages of static IP addresses
- Configuration Overhead: Configuring and managing static IP addresses can be time-consuming and labor-intensive, especially in large-scale network environments.
- Potential for Address Conflicts: Manually assigning static IP addresses increases the risk of address conflicts if multiple devices are assigned the same address inadvertently.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Business
When deciding between dynamic and static IP addresses, consider factors such as your network size, device requirements, scalability needs, and budget constraints. For businesses with dynamic network environments or limited IT resources, dynamic IP addressing may offer a more cost-effective and scalable solution. However, for devices that require consistent connectivity and remote access, static IP addressing may be the preferred choice, despite its higher maintenance overhead.
Dynamic and static IP addresses in a brief
In conclusion, dynamic and static IP addresses each have their respective advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them ultimately depends on your business’s specific requirements and priorities. By understanding the key differences between dynamic and static IP addressing and considering factors such as stability, scalability, and control, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your business needs and ensures seamless connectivity in today’s dynamic digital landscape.
For IP Address leasing and IP Address one-stop solutions, kindly visit Larus.net
Trusted IPv4 Leasing for Business Growth
Get enterprise-grade IPv4 space quickly, with seamless deployment and end-to-end management.
Get Started with i.leaseFAQs
Does a Static IP address make my internet faster?
No. A Static IP does not increase your bandwidth or raw internet speed. However, it can make the connection more stable for certain applications like web hosting, file transfers (FTP), and VoIP, which can feel faster because there is less overhead in re-establishing connections.
Can a Static IP be used with a VPN?
Yes. Many premium VPN providers offer a “Dedicated IP” service, which is a static IP address assigned exclusively to you. This is highly useful for accessing secure business networks or banking sites that might flag or block shared, dynamic VPN addresses as suspicious.
Is a Dynamic IP address safer than a Static IP?
Generally, yes. Because a Dynamic IP changes periodically, it is a “moving target” for hackers. A Static IP remains the same, making it easier for an attacker to find and repeatedly target your network if you haven’t implemented strong security measures like a firewall and DDoS protection.
Related Posts

Inbound vs. Outbound IPv4 Leasing: A Complete Guide for Enterprises
Understanding IPv4 leasing helps enterprises manage scarce address space, reducing risk and unlocking strategic growth opportunities in today’s digital economy. Key points Distinguishes between inbound (leasing in) and outbound (leasing out) IPv4 approaches and their strategic implications. Highlights contract structures, registry risk management and continuity considerations affecting global number resources. Inbound vs. outbound IPv4 leasing: complete enterprise guide In the post-exhaustion era of Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4),Read more Related Posts Inbound vs. Outbound IPv4 Leasing: A Complete Guide for Enterprises Understanding IPv4 leasing helps enterprises manage scarce address space, reducing risk and unlocking strategic growth opportunities in today’s digital economy. Key Read more Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to turn idle IPv4 addresses into a recurring revenue stream with iLease Unlock the hidden value of unused IPv4 addresses with iLease, turning dormant digital infrastructure into a recurring revenue stream while Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }

Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses
The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they fear the perceived complexity or legal “gray areas.” As IPv4 exhaustion becomes a permanent reality, the value of these addresses has skyrocketed, yet misconceptions continue to stall potential transactions. At i.lease, powered by the real-world expertise of LARUS, we’ve seen how these myths prevent companies from unlocking significant capital.Read more Related Posts Inbound vs. Outbound IPv4 Leasing: A Complete Guide for Enterprises Understanding IPv4 leasing helps enterprises manage scarce address space, reducing risk and unlocking strategic growth opportunities in today’s digital economy. Key Read more Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to turn idle IPv4 addresses into a recurring revenue stream with iLease Unlock the hidden value of unused IPv4 addresses with iLease, turning dormant digital infrastructure into a recurring revenue stream while Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }

How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker
Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global transfers. IPv4 transactions are regulated transfers, not simple purchases — registries must approve documentation, justification and registration changes. Certified brokers reduce risk and delay by aligning buyers with registry policy, routing legitimacy and cross-region requirements. Why companies still need to buy IPv4 addresses The global supply of IPv4 addressesRead more Related Posts Inbound vs. Outbound IPv4 Leasing: A Complete Guide for Enterprises Understanding IPv4 leasing helps enterprises manage scarce address space, reducing risk and unlocking strategic growth opportunities in today’s digital economy. Key Read more Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to turn idle IPv4 addresses into a recurring revenue stream with iLease Unlock the hidden value of unused IPv4 addresses with iLease, turning dormant digital infrastructure into a recurring revenue stream while Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }