Common IP Addressing Issues and Solutions 2024
In today’s interconnected world, IP addressing serves as the foundation of communication across the internet and local networks. However, with the proliferation of devices and the complexity of network configurations, organizations often encounter various challenges related to IP addressing. In this blog post, we’ll explore some of the common IP-addressing issues faced by businesses and individuals, along with practical solutions to overcome them.
Table of Contents
Understanding IP Addressing
Before delving into the specific issues and solutions, it’s essential to understand the basics of IP addressing. An IP address, or Internet Protocol address, is a numerical label assigned to each device connected to a network. It enables devices to communicate with each other and facilitates the exchange of data packets across networks. IP addresses are categorized into two main types: IPv4 and IPv6, each with its unique characteristics and limitations.
Common IP Addressing Issues
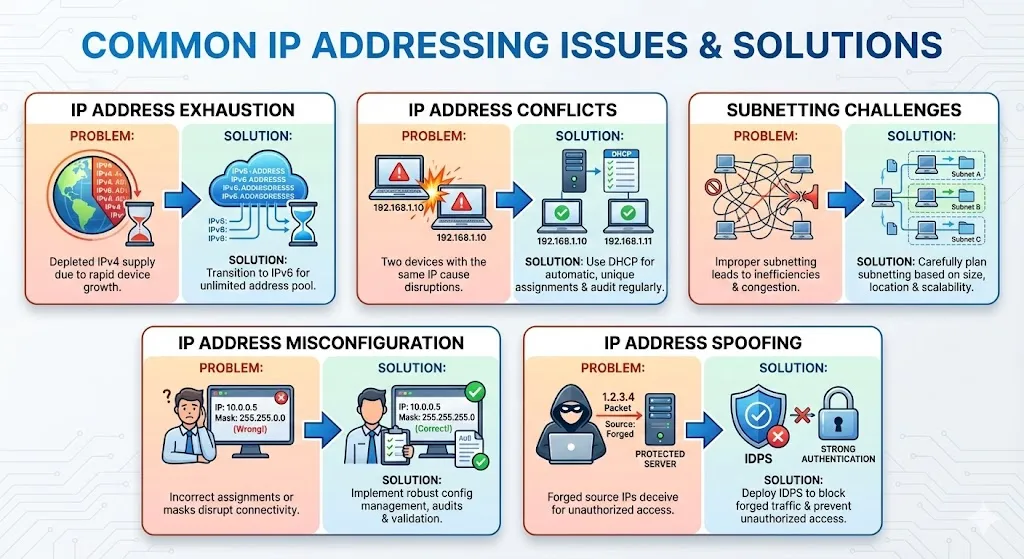
IP Address Exhaustion:
- With the rapid growth of internet-connected devices, the supply of available IPv4 addresses has depleted significantly, leading to address exhaustion.
- Solution: Transition to IPv6, which offers a virtually unlimited pool of IP addresses to accommodate the increasing demand.
IP Address Conflicts:
- IP address conflicts occur when two devices on the same network are assigned the same IP address, resulting in communication issues and network disruptions.
- Solution: Implement proper network management practices, such as using DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) to automatically assign unique IP addresses to devices and regularly auditing the network for conflicts.
Subnetting Challenges:
- Subnetting involves dividing a large network into smaller, more manageable subnetworks. However, improper subnetting can lead to inefficiencies and network congestion.
- Solution: Plan and design subnetting schemes carefully, taking into account factors such as network size, geographical location, and future scalability requirements.
IP Address Misconfiguration:
- Misconfigurations, such as incorrect IP address assignments or subnet masks, can disrupt network connectivity and lead to security vulnerabilities.
- Solution: Implement robust network configuration management practices, including regular audits, documentation, and validation checks, to ensure accurate IP address assignments and configurations
IP Address Spoofing:
- IP address spoofing involves forging the source IP address of network packets to deceive recipients and gain unauthorized access to networks.
- Solution: Deploy intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) to detect and block spoofed IP traffic, along with implementing strong authentication mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access.
Practical Solutions for IP Addressing
1. IPv6 Adoption:
Transitioning to IPv6 enables organizations to future-proof their networks and overcome the limitations of IPv4 address exhaustion.
Encourage IPv6 adoption through education, training, and collaboration with internet service providers (ISPs) and network equipment vendors.
2. Network Automation:
Implement network automation tools and solutions to streamline IP address management processes, automate repetitive tasks, and reduce the risk of human error.
Utilize technologies such as software-defined networking (SDN) and network orchestration platforms to automate IP address provisioning, configuration, and monitoring.
3. IP Address Management (IPAM) Solutions:
Invest in IPAM solutions that provide centralized management and control of IP address assignments, subnetting, and DNS (Domain Name System) integration.
Choose IPAM solutions that offer scalability, flexibility, and support for both IPv4 and IPv6 addressing schemes.
In A Nutshell
Navigating the complexities of IP addresses requires a proactive approach, robust network management practices, and the adoption of emerging technologies. By addressing common IP issues and implementing practical solutions, organizations can optimize network performance, enhance security, and ensure seamless connectivity in the digital landscape. Embracing IPv6 adoption, leveraging network automation, and deploying IPAM solutions are key steps toward building resilient and future-ready networks in the ever-evolving world of technology.
Trusted IPv4 Leasing for Business Growth
Get enterprise-grade IPv4 space quickly, with seamless deployment and end-to-end management.
Get Started with i.leaseFAQs
What is the fastest way to fix an IP address conflict?
The most immediate solution is to release and renew your IP address.
- Windows: Open Command Prompt and type
ipconfig /releasefollowed byipconfig /renew. - Mac/Mobile: Turn your Wi-Fi off and back on. If the issue persists, you may need to check if any device has been manually assigned a static IP that overlaps with the DHCP pool.
How do I know if my IP address has been spoofed?
Detecting a single spoofed packet is difficult for individuals, but organizations can look for “Inconsistent Traffic Patterns” in their firewall logs—such as internal IP addresses appearing to originate from an external network interface. Implementing Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding (uRPF) is a standard technical solution to block these forged packets.
Can I solve IPv4 exhaustion without moving to IPv6 yet?
While IPv6 is the long-term goal, many businesses use IPv4 Leasing as a bridge solution. This allows you to rent a clean block of IPv4 addresses instantly, giving you the resources needed to grow your infrastructure while you plan a gradual migration to IPv6.
Related Posts

Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses
The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they fear the perceived complexity or legal “gray areas.” As IPv4 exhaustion becomes a permanent reality, the value of these addresses has skyrocketed, yet misconceptions continue to stall potential transactions. At i.lease, powered by the real-world expertise of LARUS, we’ve seen how these myths prevent companies from unlocking significant capital.Read more Related Posts Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global Read more What happens when IP resources are mismanaged Poor IP resource management can lead to outages, security breaches, blacklisting, legal exposure and reputational damage across networks and business Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }

How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker
Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global transfers. IPv4 transactions are regulated transfers, not simple purchases — registries must approve documentation, justification and registration changes. Certified brokers reduce risk and delay by aligning buyers with registry policy, routing legitimacy and cross-region requirements. Why companies still need to buy IPv4 addresses The global supply of IPv4 addressesRead more Related Posts Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global Read more What happens when IP resources are mismanaged Poor IP resource management can lead to outages, security breaches, blacklisting, legal exposure and reputational damage across networks and business Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }

How to turn idle IPv4 addresses into a recurring revenue stream with iLease
Unlock the hidden value of unused IPv4 addresses with iLease, turning dormant digital infrastructure into a recurring revenue stream while navigating market demand, compliance and risk. Leasing idle IPv4 blocks can generate steady, long-term income without relinquishing ownership. Platforms like i.lease global IPv4 marketplace make it easier to monetise addresses and manage reputation and compliance. why IPv4 addresses still matter Despite the long-anticipated exhaustion of the IPv4 address space — aRead more Related Posts Common Myths About Selling IP Addresses The IPv4 secondary market is often shrouded in mystery, leading many organizations to sit on valuable digital assets because they Read more How to buy IPv4 addresses through a certified IP broker Buying IPv4 space requires policy compliance, verified need, and registry approval, making certified IP brokers essential guides through complex global Read more What happens when IP resources are mismanaged Poor IP resource management can lead to outages, security breaches, blacklisting, legal exposure and reputational damage across networks and business Read more .related-post {} .related-post .post-list { text-align: left; } .related-post .post-list .item { margin: 5px; padding: 10px; } .related-post .headline { font-size: 18px !important; color: #999999 !important; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_thumb { max-height: 220px; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_title { font-size: 16px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } .related-post .post-list .item .post_excerpt { font-size: 13px; color: #3f3f3f; margin: 10px 0px; padding: 0px; display: block; text-decoration: none; } @media only screen and (min-width: 1024px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 30%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 0px) and (max-width: 767px) { .related-post .post-list .item { width: 90%; } }