What is GeoIP and How Does It Work?

GeoIP is crucial in tailoring online experiences, improving cybersecurity, and powering countless business applications. But what exactly is GeoIP, how does it work, and why is it so important? Let’s dive in.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is GeoIP?
GeoIP stands for “Geographical Internet Protocol.” It refers to the technology that determines a user’s geographic location based on their IP (Internet Protocol) address. Every device connected to the Internet is assigned a unique IP address, which acts like a digital identifier. GeoIP leverages this information to pinpoint the device’s physical location, often revealing the country, region, city, and Internet service provider (ISP).
How Does GeoIP Work?
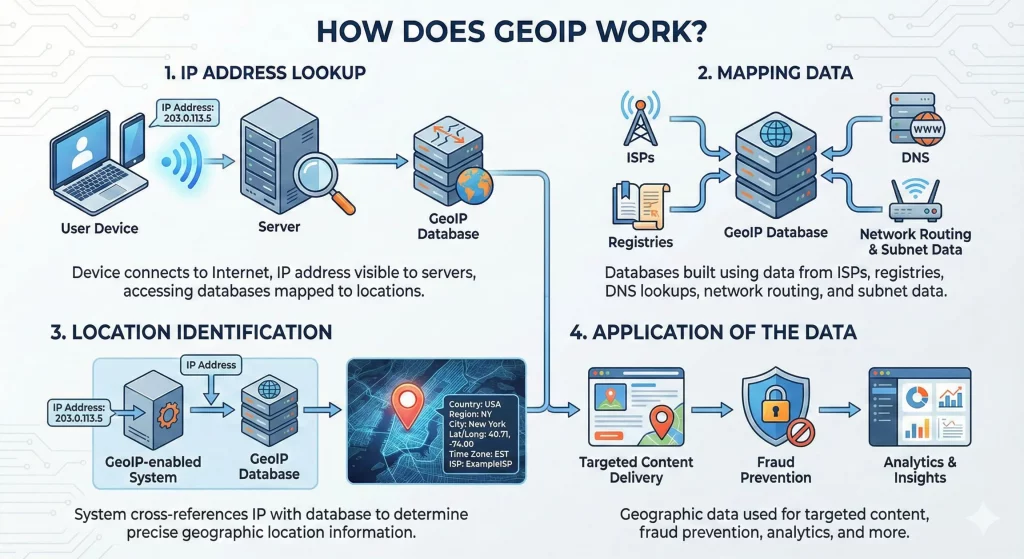
The functionality of GeoIP can be summarized in a few steps:
1. IP Address Lookup
When a device connects to the Internet, its IP address becomes visible to the servers it interacts with. GeoIP technology accesses vast databases of IP addresses mapped to specific geographic locations.
2. Mapping Data
GeoIP databases are built using data from ISPs, registries, and third-party providers. These databases link each IP address to a geographic location based on information like Internet service provider details, DNS (Domain Name System) lookups network routing, and subnet data
3. Location Identification
When a GeoIP-enabled system detects an IP address, it cross-references the address with the database to determine the location. The output may include information such as:
Country, region/state, city, latitude, and longitude (approximate), time zone, ISP organization name.
4. Application of the Data
The geographic data is used for various purposes, such as targeted content delivery, fraud prevention, or analytics.
Significance of GeoIP in the Digital World
GeoIP has become an indispensable tool across multiple industries, offering benefits in areas such as:
1. Personalized Content Delivery:
Websites and apps use GeoIP to customize user experiences, such as showing location-specific language options, currency displays, or tailored recommendations.
2. Digital Marketing:
Marketers leverage GeoIP to serve hyperlocalized ads, ensuring ad campaigns are more relevant and effective.
3. Cybersecurity:
GeoIP is vital for detecting and mitigating online threats. For example, unusual login attempts from regions where a user is not typically active could trigger security alerts.
4. Regulatory Compliance:
Businesses operating in multiple countries use GeoIP to enforce location-based restrictions, such as GDPR compliance in the EU or content licensing regulations for streaming platforms.
5. Fraud Detection and Prevention:
E-commerce platforms and payment gateways rely on GeoIP to identify potentially fraudulent transactions, such as mismatches between billing addresses and IP locations.
6. Traffic Analytics:
GeoIP enhances web analytics by providing insights into where users are coming from, helping businesses optimize their reach.
Challenges and Limitations
- Accuracy Issues: GeoIP data may not always be precise, especially at the city or street level.
- VPNs and Proxies: Users masking their IP addresses with virtual private networks (VPNs) or proxies can bypass GeoIP detection.
- Database Updates: GeoIP databases require regular updates to stay accurate as IP address assignments change.
Conclusion
GeoIP bridges the gap between the digital and physical worlds by providing location-based insights. Whether you’re running a global e-commerce site, ensuring compliance with local laws, or simply delivering personalized content, GeoIP technology enhances efficiency, security, and user satisfaction in countless ways. However, as the technology evolves, businesses must balance its potential with considerations for accuracy, privacy, and ethical use.
Trusted IPv4 Leasing for Business Growth
Get enterprise-grade IPv4 space quickly, with seamless deployment and end-to-end management.
A clear comprehension of the discrepancies between IP reputation and IP risk score constitutes a critical prerequisite for effective cybersecurity Read more
Organisations increasingly rely on IP risk scores. They use them to assess threat levels. They reduce fraud losses. They strengthen Read more
The current era faces IPv4 address scarcity. Organizations must verify IP block risk scores. Tools like i.lease help complete this Read more



